If you’re looking to build wealth and financial stability, diversifying your streams of income can be a powerful strategy. By generating multiple sources of revenue, you can reduce your reliance on any single income stream and increase your earning potential over time.
In this blog post, we’ll explore 7 different streams of income that can help you achieve financial independence and build long-term wealth. From passive income streams like real estate income and dividend stocks to more active income streams like entrepreneurship and royalties, there are a variety of ways to increase your earning potential and secure your financial future.
So whether you’re looking to supplement your current income or build a sustainable long-term wealth plan, these 7 streams of income can help you achieve your financial goals. Let’s dig in.
1. Earned Income
Earned income is the most common and traditional form of income that most people receive through their employment. Earned income is the money you get in exchange for the time and effort that you put into your job. This stream of income is often characterized by a fixed hourly wage, annual salary, or commission-based pay.
One of the benefits of earned income is that it generally provides a consistent and reliable source of income that allows you to cover your basic living expenses and save for your future. This is also where most people start before building out other incomes streams in the future.
However, the downside of earned income is that your earning potential can be limited by your employer, your industry, and your time. In addition, though earned income is consistent for most people most of the time, there is lots of risk associated with relying on it as your only source of income. In the event that you lose your job, it can be stressful if you have no other source of income.
Nevertheless, if you want to maximize your earned income, you should focus on developing and improving your skills and expertise, networking with professionals in your industry, and pursuing career advancement opportunities. This may include getting additional education and certifications, seeking promotions or leadership positions, and/or even transitioning to a higher-paying job or industry.
Overall, earned income is where most of us start building out our income streams and an area that can’t be ignored if you want to start building wealth.
Earned Income Summary
- Pros: Reliable. Easier to obtain.
- Cons: Limited by time. Doesn’t scale. Can be risky as sole income source.
2. Capital Gains
Capital gains are profits that you make from selling an asset, such as stocks, real estate, or artwork, at a higher price than you originally paid for it. This form of income is often associated with long-term investing and is an effective way to build wealth over time.
The amount of capital gains you can earn depends on the value of the asset when you sell it and how much you paid for it initially. Additionally, if you hold an asset for more than a year before selling it, you will be taxed at the long-term capital gains rate, which is typically lower than the tax rate you would need to pay on ordinary income.
In fact, a single individual using the standard deduction in 2022 would pay $0 in federal taxes (yes $0!) if their adjusted gross income was $54,625 (or less) and was completely from long-term capital gains. For married couples, this number jumps to over $100,000 in tax-free capital gain income when using the standard deduction.
Of course, since most people generate earned income throughout their lives, this strategy is best for those in retirement who can sell down their assets without having to pay Uncle Sam.
Another benefit of capital gains income is that it requires relatively little effort on your part once you’ve set it up. Though saving money to invest can be hard, generating capital gains after you’ve invested your money is a form of truly passive income that can help you build wealth.
The big downside of capital gains income is that it can disappear quickly, especially for newer investors. Though markets tend to go up most of the time, during downturns you can see your capital gains quickly turn into capital losses. Keep this in mind before relying on capital gains as a long-term income source.
To maximize your capital gain income, you should continually invest in a well-diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other income-producing assets and then hold them for the long-term.
Capital Gains Summary
- Pros: Passive. Better tax treatment.
- Cons: Can disappear quickly. Not as reliable. Requires capital.
3. Interest Income
Interest income is another form of passive income that is generated by lending money to others, typically through a savings account, money market account, certificates of deposit, or fixed income securities. This form of income can be a reliable and predictable source of revenue, as the interest rate is typically fixed and earned over a set period of time.
One of the benefits of interest income is that it is generally considered a low-risk investment that provides a guaranteed rate of return. This makes it an attractive option for individuals who want to earn a steady stream of income without the volatility and risk of other investments.
To maximize your interest income, you can shop around for high-yield savings accounts or CDs that offer competitive interest rates. You can also consider investing in government or corporate bonds, which can provide higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts.
However, it’s important to recognize that interest income is subject to inflation risk. While prices may rise, your interest payments are fixed. And if the rate of inflation is higher than the interest rate you are being paid, then the purchasing power of your income will go down over time even if you are reinvesting that income.
Lastly, interest income is subject to income tax (sometimes at both the federal and state level), which can further reduce your earnings.
Overall, interest income can be a useful stream of income to supplement your other income sources as you continue to build your wealth. And with short-term Treasury rates hovering around 5%, there’s never been a better time in recent years to consider adding this income source to your portfolio.
Interest Income Summary
- Pros: Passive. Consistent and predictable.
- Cons: Requires capital. Small relative to other income sources.
4. Dividend Income
Dividend income is a form of passive income that is earned by owning stocks that pay dividends, which are a portion of the company’s profits that are distributed to shareholders. Dividend income is often considered a more stable form of income compared to capital gains, as it is not tied to the fluctuations of the stock market and can provide a consistent stream of revenue over time.
For example, during the Great Depression, U.S. stock prices declined by 90% yet dividend income dropped by less than 50%. This illustrates how dividend income can act as a partial buffer against large declines in asset prices. This does not mean that dividend income is guaranteed, as companies can reduce or eliminate their dividends at any time. However, it is far stickier than many realize.
More importantly, compared to other forms of income, dividend income is more likely to keep pace with inflation as companies raise their dividends to offset higher prices. Once again, this isn’t guaranteed, but it isn’t unusual either.
To maximize your dividend income, you can invest in high-quality dividend-paying stocks that have a history of consistent dividend payouts and a track record of stable earnings. You can also consider investing in dividend-focused mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) to gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of dividend-paying stocks.
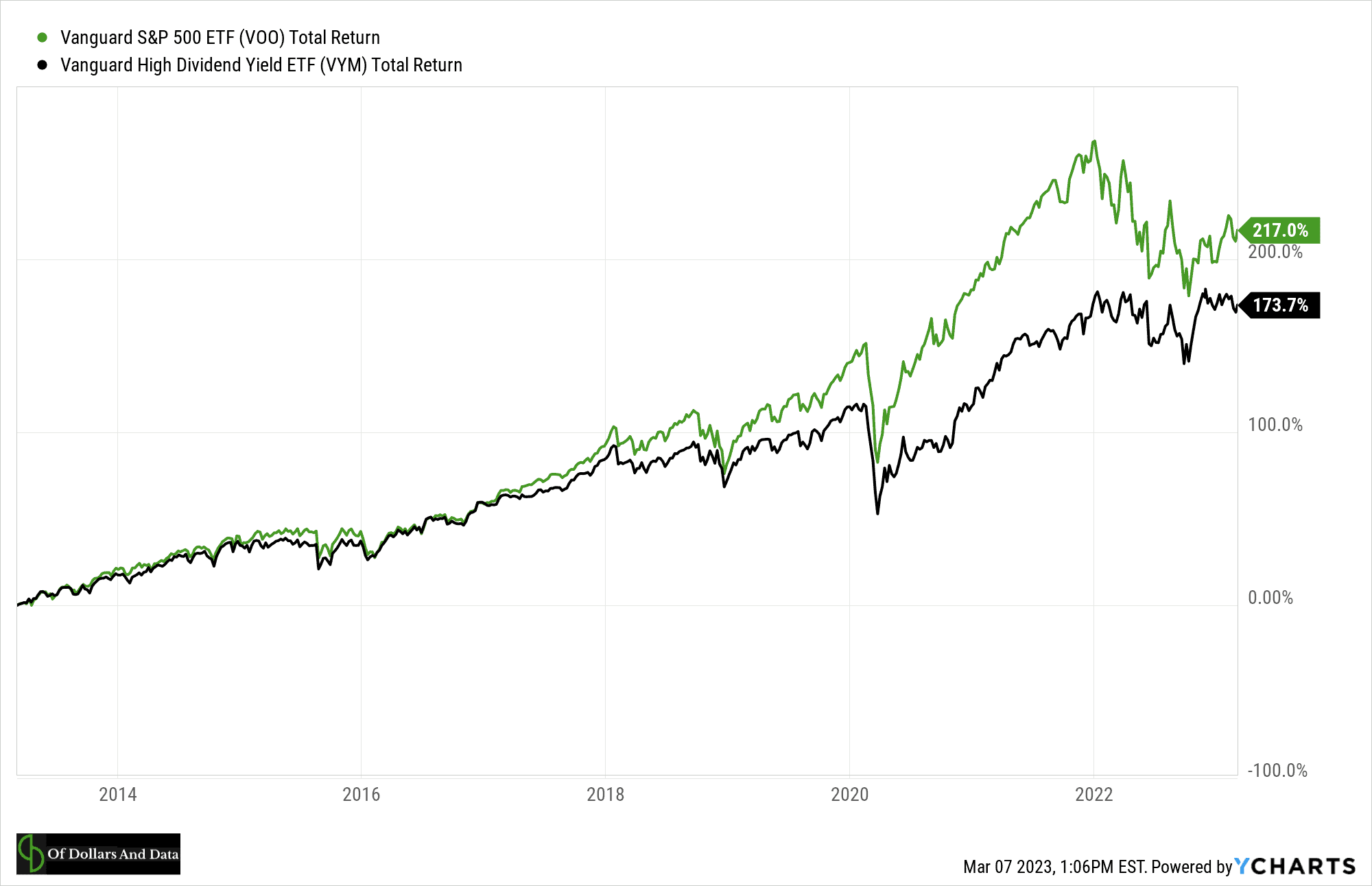
The one downside of owning dividend stocks is that they have underperformed the market in recent years. As you can see in the chart below, the Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF has underperformed the S&P 500 by ~44% over the last 10 years (on a total return basis):
This is a big reason why I am generally not a fan of dividend investing. Owning them has come at a cost in recent years.
Despite their underperformance, I still understand their appeal. The income stream associated with dividend stocks is likely to be far more stable during market downturns than the price of an overall stock portfolio. Therefore, if you are someone who likes the idea of a more stable income stream, then dividend investing might provide the psychological comfort that an overall market portfolio simply can’t.
Either way, dividend income can be useful for those who want another passive stream of income.
Dividend Income Summary
- Pros: Passive. Relatively stable.
- Cons: Requires capital. May not generate as much income (long-term) as stocks generally.
5. Rental Income
Rental income is a form of passive income that is earned by owning and renting out a property, such as a house, apartment, or commercial space. This form of income can provide a steady and reliable source of revenue, as rental income is typically earned on a monthly basis and can be used to pay off the mortgage or other expenses associated with the property.
One of the benefits of rental income is that it can provide a hedge against inflation, as rental income can increase over time with the rising cost of living. Additionally, rental income can provide a tax benefit, as rental expenses, such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and maintenance costs, can be deducted from your rental income.
To maximize your rental income, you can invest in a property that has the potential for high rental demand, such as a property in a desirable location or with unique amenities. You can also consider hiring a property manager to handle the day-to-day operations of the property and ensure that the rental income is maximized.
However, it’s important to recognize that rental income is not without risk and hassle. You may experience periods of vacancy or have difficulty finding reliable tenants, which can reduce your overall earnings. Additionally, owning a rental property requires a level of time, effort, and investment, and may not be suitable for everyone.
For these reasons, I have generally avoided rental properties as I find the “return on hassle” isn’t worth the additional income. Note that this is a personal bias of mine and I know many investors that are quite pleased with their experience in rental properties.
In full, rental income can be useful for those who have the time, resources, and interest in owning and managing rental properties and tenant relationships.
Rental Income Summary
- Pros: Can be somewhat passive. Better tax treatment.
- Cons: Requires capital and some expertise. Mental hassle. Dealing with tenants isn’t always easy.
6. Business Income
Business income is a form of earned income that is generated by owning and operating a business. This form of income can provide unlimited potential for revenue and can be a powerful tool for building wealth over time.
One of the benefits of business income is that it can provide flexibility and independence, as you are able to control your own schedule and make decisions that can directly impact your earnings. Additionally, owning a business can provide tax benefits, as certain expenses can be deducted from your income and reduce your overall tax liability.
To maximize your business income, you can invest in a business that has a strong potential for growth and profitability.
In particular, I’ve found that online businesses are great for getting started because costs are generally lower and margins can be quite high. You can also consider leveraging technology and social media to reach more customers and generate more revenue.
However, it’s important to recognize that owning a business can also come with risk, such as market fluctuations, competition, and operational costs. Additionally, running a business requires a certain level of time, effort, and investment that may not be suitable for you.
Overall, business income can be a useful stream of income for individuals who have a passion for entrepreneurship and the drive to succeed.
Business Income Summary
- Pros: Better tax treatment. Scales well (especially if the business is online).
- Cons: Requires lots of work, capital, or both. Can take many years before you see results.
7. Royalty Income
Royalty income is a form of passive income that is earned by owning and licensing intellectual property, such as patents, copyrights, or trademarks. This form of income can provide a steady and reliable source of revenue, as royalty income is typically earned on a regular basis, based on the usage or sales of the intellectual property.
One of the benefits of royalty income is that it can provide a consistent source of income without the need for ongoing maintenance or investment. Additionally, owning intellectual property can provide a level of protection and security, as it can prevent others from using or profiting from your creative works.
To maximize your royalty income, you can invest in intellectual property that has the potential for high demand and widespread usage, such as a popular song or book. You can also consider partnering with a licensing agency or publisher to handle the licensing and distribution of your intellectual property as well.
However, it’s important to recognize that royalty income is not without risk, as the demand and popularity of intellectual property can fluctuate over time. Additionally, the process of acquiring and maintaining intellectual property can be time-consuming and require a level of investment that may not always pan out.
Royalty Income Summary
- Pros: Passive. Scale very well.
- Cons: Requires a product with demand. No guarantee of a return on your time/effort/investment.
Do You Need All 7 Streams of Income?
While having multiple streams of income can be a great way to build wealth and achieve financial freedom, it’s important to recognize that you don’t need to have all 7 streams of income to build wealth. For example, I only have six of the 7 streams of income mentioned above (sorry rental properties) and that’s fine by me.
More importantly, having one big income stream can be more impactful than many small income streams. For example, earning a high salary or running a successful business can provide a significant source of income that can be used to invest in other income-producing assets in the future.
And for many people, this is the norm. By focusing on building a strong foundation, you can then leverage this income to build other income streams when the time is right.
Regardless of what you decide to do, finding the right income streams for your lifestyle and personality is far more important than having more of them.
With that being said, happy earning and thank you for reading!
If you liked this post, consider signing up for my newsletter.
This is post 338. Any code I have related to this post can be found here with the same numbering: https://github.com/nmaggiulli/of-dollars-and-data